NoSQL Databases
Introduction
In recent years, NoSQL databases have gained widespread popularity among organizations looking to manage large, unstructured data sets. Traditional relational databases use a fixed schema and SQL language. On the other hand, NoSQL databases offer a flexible, non-relational approach to data management.
In this post, we will introduce you to the basics. So, you will find their history, key features, and differences from relational databases.
2 Categories of Databases
Databases are basically divided into two categories.
1- Relational Databases (SQL)
2- No-relational Databases (NoSQL)
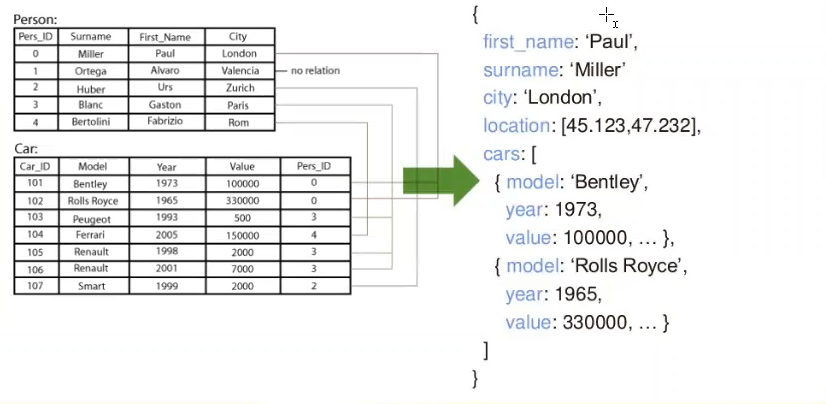
First, we look at what SQL and NoSQL look like. In this visual, we can observe how the same tables look in both types
Differences of SQL and NoSQL Databases
SQL
NoSQL
Models are relational in nature.
Models are not relational.
There are no schema conditions to follow.
The data is stored in tables.
Data can be stored in JSON, key/value, etc.
It is suitable for cases where every record is of the same type and has the same properties.
Each record does not need to have the same attribute, which makes the database very flexible.
Adding a new property means we have to change the whole schema.
New attributes can be easily added to the data.
Schemas are very rigid.
There are no schema conditions to follow.
A Brief History of NoSQL Databases
The term “NoSQL” was first coined in the late 1990s, as a response to the limitations of traditional relational databases in handling large, unstructured data sets. In the early days, they were mostly used for niche applications, such as gaming and social media.
However, as big data and the Internet of Things (IoT) emerged, they gained wider acceptance as a more scalable and flexible solution for managing large and complex data.
Key Features of NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases are known for their ability to handle large and unstructured data sets, but there are several other key features that set them apart from traditional relational databases:
- Flexibility: They offer a flexible, non-relational approach to data management, allowing organizations to store and manage data in a variety of formats, including text, images, and multimedia.
- Scalability: They are designed to scale horizontally, meaning that they can handle an increased volume of data and traffic by adding more nodes to the system.
- Performance: They are optimized for high performance, with features such as indexing and caching that can significantly improve query speed and response times.
- Cost savings: They are often less expensive to maintain and scale than traditional relational databases, making them an attractive solution for organizations looking to reduce costs.
Key Terminology of NoSQL
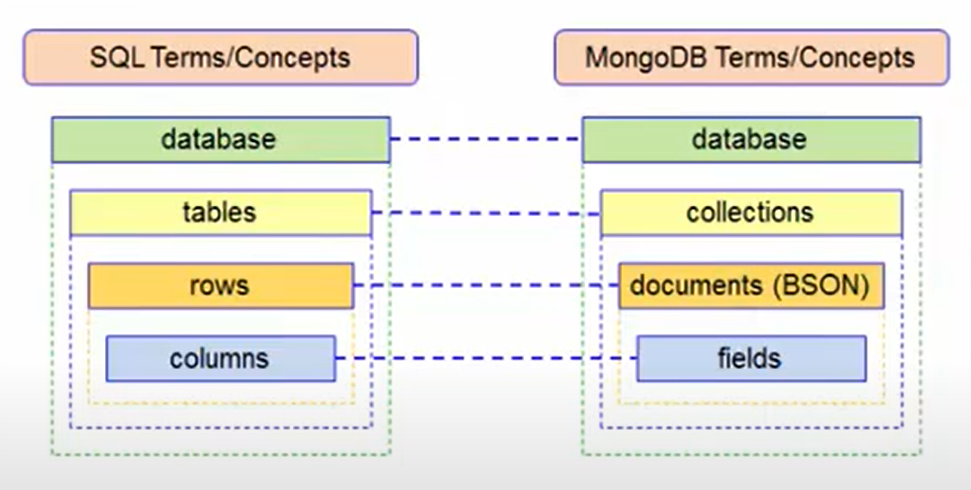
- Database: t is a large data storage area, usually containing multiple collections. It holds all of the data in an application or system.
- Collections: It means logical groups of data in a database. Each collection contains similar types of documents or records.
- Documents: It represents each data record in a collection. They are usually structured in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) or BSON (Binary JSON) format. Each document has a unique identifier (ID) within the collection and can consist of different fields.
- Fields: These are pieces of data inside documents. Each field carries a specific type of data and defines the properties of a document.
Types of NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases come in several different flavors, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
- Document databases: Document databases, such as MongoDB and CouchDB, store data in a hierarchical structure similar to JSON or XML. They are well-suited for handling complex and nested data structures, such as those found in web applications and IoT devices.
- Key-value stores: Key-value stores, such as Redis and Riak, store data as a collection of keys and values. They are optimized for fast read and write operations, making them a popular choice for caching and session management.
- Column-oriented databases: Column-oriented databases, such as Apache Cassandra and Hbase, store data in columns instead of rows. This allows them to handle large amounts of data with a high degree of parallelism, making them well-suited for big data applications.
- Graph databases: Graph databases, such as Neo4j and Amazon Neptune, store data as nodes and edges in a graph structure. They are ideal for handling complex relationships between data, such as those found in social networks and recommendation systems.
Conclusion
NoSQL databases have emerged as a powerful solution for organizations looking to manage large and complex data sets. With their flexible, scalable, and high-performing architecture, they offer a more cost-effective alternative to traditional relational databases.
If you’re considering a NoSQL solution for your data management needs, consider reaching out to Mysoly, a data management company that can provide the expertise and guidance you need to succeed.